Bronchiectasis

Bronchiectasis is a chronic condition where the airways (bronchi) of your lungs are inflamed, infected, and permanently damaged.
Chest Infection

A chest infection is an invasion of pathogens affecting the bottom part of your respiratory tract (lungs) including the windpipe, bronchi, and lungs. Infections can range from mild to severe. Pathogens may include bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites that are not normally present within the body.
Chronic Bronchitis

Bronchitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of mucous membranes that line airway passages in the lungs. The mucous membranes swell and grow thicker, narrowing and blocking the airway, making it difficult to breathe. Bronchitis lasting more than 3 months for two consecutive years is termed chronic.
Chronic Cough

Coughing is the voluntary or involuntary rapid expulsion of air from the lungs to clear the throat and breathing passages of mucus or other irritants. A cough that lasts for more than 8 weeks is a chronic cough. It may be a sign of an illness or certain diseases of the lungs, stomach, heart or nervous system.
Chronic Respiratory Failure

Chronic respiratory failure is the inability to carry out the fundamental functions of respiration. The lungs function to deliver oxygen to the blood while eliminating carbon dioxide from the blood. It is a condition that usually occurs from narrow or damaged airways that develop gradually over time with a progressive underlying process that requires long-term treatment.
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)

COPD is a progressive and chronic inflammatory disease of your lungs. The condition leads to obstructed airflow from the lungs making it harder for you to breathe.
Coronavirus (COVID-19)

Coronaviruses belong to a large group of viruses that are known to cause severe respiratory illness ranging from the common cold to more serious illnesses such as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) or Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) in humans. Coronaviruses are commonly found in animals such as civet cats and camels and are known to be transmitted between animals and humans.
Pleural Effusion

The thin membranes that line the lungs and the inside of the chest cavity, which help to lubricate and facilitate breathing, are called pleura. In some cases, an excess amount of fluid may develop between the layers of the pleura outside the lungs. This is known as pleural effusion.
Pulmonary Fibrosis

Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease that causes damage and scarring in the tissue of the lungs. This build-up of scar tissue makes your lungs thick and stiff, making it difficult to breathe.
Restrictive Lung Diseases

Restrictive lung diseases are chronic medical conditions that limit the ability of the lungs to expand during inhalation causing reduced lung capacity or volume that increases an individual’s breathing rate to meet the oxygen demand. In most cases, they are found to be progressive and worsen over time.
Shortness of Breath

Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, is discomfort or difficulty in breathing or the inability to get enough air to breathe. It can occur suddenly or gradually over a period of time and can be classified into acute or chronic shortness of breath respectively.
Central Sleep Apnea

Central sleep apnea is a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep due to insufficient stimulation from the brain. It is a rare form of sleep apnea.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea

Obstructive sleep apnoea describes a sleep disorder characterized by frequent pauses in breathing due to collapse or obstruction of the airway. It is quite a common disorder and affects around 4% of the population.
Endobronchial Ultrasound

Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) is a technique that helps in the diagnosis and evaluation of the stage of lung cancer. It helps visualize airway walls and other adjoining structures. The endobronchial ultrasound helps to visualize the different layers of the bronchial wall with mucosa, submucosa, endochondrium, cartilage, perichondrium, connective tissue, and adventitia.
Non-Invasive Ventilation

Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) refers to the administration of mechanical ventilation to the lungs using methods such as a face mask, without the need of an invasive artificial airway, such as an endotracheal tube (ETT) or tracheal tube (TT).
Recurrent Coughs and Colds

A cold is mainly caused by a viral infection of your child’s nose and throat (upper respiratory tract). A cough is the body's way of removing irritants from the airway. Although colds and coughs normally clear on their own, sometimes a child may experience frequent or recurrent episodes that can be distressing.
Recurrent Respiratory Infections

Respiratory infection is a disease of the respiratory tract, the airway passage that begins at the nose, passes through the throat and ends in the lungs. Respiratory tract infections are mainly caused by viruses and occasionally bacteria.
Lung Cancer

Cancer is a disease that results from abnormal growth and division of cells that make up the body's tissues and organs. Under normal circumstances, cells reproduce in an orderly fashion to replace old cells, maintain tissue health and repair injuries.
COVID-19 Diagnosis and Management

COVID-19 is a respiratory disease caused by a virus belonging to the Coronavirus family known as SARS-CoV-2 or Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Since it first emerged in December 2019, COVID-19 has caused millions of deaths around the world.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)

Respiratory syncytial virus or RSV is a common and contagious virus that affects people of all ages. Among children and infants, the infection is most common. For many adults and healthy children, RSV symptoms are similar to those of a common cold.
Asthma
Air is supplied to the lungs for purification through narrow tubes. When these tubes get inflamed and narrowed, it leads to a chronic condition called asthma. Asthma can be triggered by allergens (pollen, mold and fur), cold air and changes in weather, exercise, flu, and the common cold.
Bronchoscopy
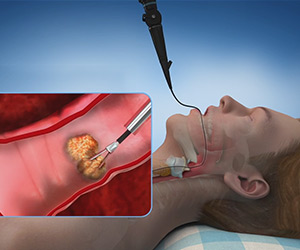
Bronchoscopy is a procedure used to evaluate the airways, lungs or lymph nodes in the chest for abnormalities and to treat conditions such as abnormal growths or foreign bodies causing airway obstruction.
